Northern Hemisphere Snow Cover Extent
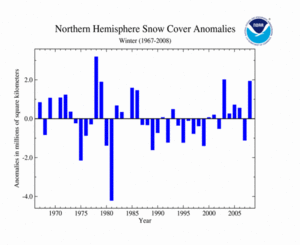
As shown in the time series to the right, the mean Northern Hemisphere snow cover extent during winter 2007/2008 was above average. This can be primarily attributed to the multiple snow and ice storms that affected much of the Northern Hemisphere during the winter. This resulted in the 4th largest snow cover extent on record. The mean Northern Hemisphere winter snow cover extent for the 1967-2008 period of record was 45.5 million square kilometers.
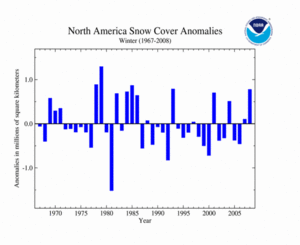
Across North America, snow cover for winter 2007/2008 was above average, the 6th largest extent since satellite records began in 1967. A series of snow and ice storms struck the U.S. since the beginning of winter. The heavy snowfall during the winter prompted more than 4,700 new daily snowfall records and several new seasonal records across the contiguous U.S. The mean North America winter snow cover extent was 17.1 million square kilometers for the 1967-2008 period of record.
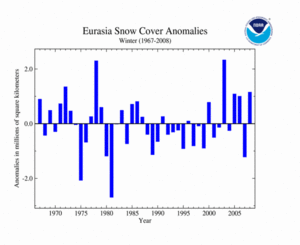
As depicted in the time series to the right, Eurasia's snow cover extent during winter 2007/2008 was above average. During January 2008, China suffered its worst severe winter weather in 5 decades. Although analysis of the causes of unusually severe winter storms in southern China continues, scientists at NOAA's Earth System Research Laboratory have early indications that the severe weather may have been due to the presence of unusually strong and persistent high pressure over Eastern Europe combined with low pressure over Southwest Asia. This pattern directed a series of storms across the region while northerly low level flow introduced cold air from Mongolia. Unusually warm water temperatures in the China Sea may have provided a favorable environment of available moisture that enhanced the severity of these storms. Also, parts of the Middle East region experienced their heaviest snowfall in more than a decade while other areas saw snow fall for the first time in living memory. In February 2008, severe winter weather continued to affect much of Eurasia, prompting the winter 2007/2008 to have the 4th largest snow cover extent over the 41-year historical period. On average, the Eurasian boreal winter snow cover extent was 28.4 million square kilometers for the 1967-2008 period of record.
Data were provided by the Global Snow Laboratory, Rutgers University.
Sea Ice Extent
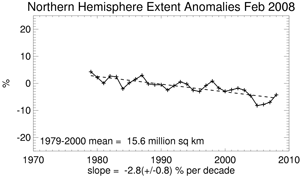
According to the National Snow and Ice Data Center, the February 2008 Northern Hemisphere sea ice extent, which is measured from passive microwave instruments onboard NOAA satellites, was below the 1979-2000 mean, but greater than the previous four years. This was the fifth least February sea ice extent on record. Including 2008, the past five years had the least February sea ice extent since records began in 1979. Sea ice extent for February has decreased at a rate of 2.8%/decade (since satellite records began in 1979) as temperatures in the high latitude Northern Hemisphere have risen at a rate of approximately 0.37°C/decade over the same period.
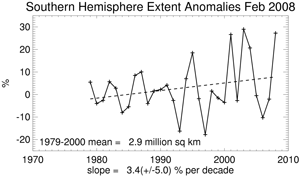
Meanwhile, the February 2008 Southern Hemisphere sea ice extent was much above the 1979-2000 mean. This was the second largest sea ice extent in February (27% above the 1979-2000 mean) over the 30-year historical period, behind 2003. Sea ice extent for February has increased at a rate of 3.4%/decade.
For further information on the Northern and Southern Hemisphere snow and ice conditions, please visit the NSIDC News page, provided by the NOAA's National Snow and Ice Data center (NSIDC).
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information