National Temperature - Summer
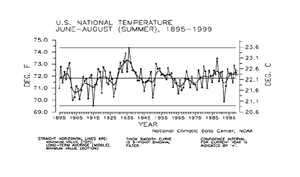
Preliminary data for Summer (June-August) 1999 indicate the mean temperature for the three-month period averaged across the contiguous United States was above the long-term mean. Nearly six percent of the country was much warmer than normal while about one percent of the country averaged much cooler than normal. Five of the last six summer seasons have been above the long-term mean.
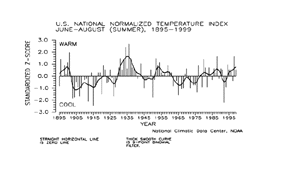
The national temperature index expresses temperature departure from the 60-year mean in terms of standard deviations. Each year's temperature value is standardized for each of 344 climate divisions in the U.S. by using their 1931-90 means and standard deviations, then weighting these divisional values by area. These area-weighted values are then normalized over the period of record. Positive values are warmer and negative values are cooler than the mean.
| The preliminary national standardized temperature index also ranked Summer 1999 above the long term mean.
|
larger image
|
larger image
|
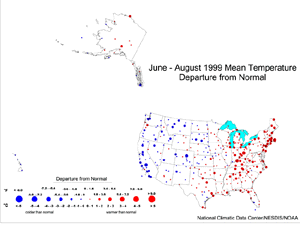
The map to the left, based on approximately 250 airport stations, shows Summer (June-August) 1999 average temperatures as a departure from 1961-1990 station normals. The overall pattern consisted of widespread warmth from the southern Plains to the Northeast, and generally below-normal average summer temperatures from the northern Rockies to southern California, with a mixed pattern in the transition area between these two. The Hawaiian stations averaged slightly cooler than normal, while Alaska was near to above normal.
|

National Precipitation - Summer
larger image
|
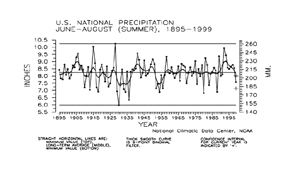
Preliminary data for Summer (June-August) 1999 indicate the three-month precipitation averaged across the contiguous United States was much drier than normal and ranked as the 22nd driest summer since 1895. Nearly 13% of the country was much drier than normal while about six percent of the country was much wetter than normal. Summer 1999 was the first such season since 1988 to be much drier than normal.
|
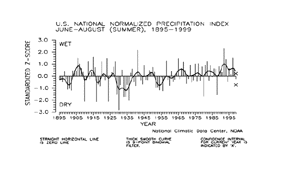
The national precipitation index expresses precipitation departure from the 60-year mean in terms of standard deviations. Each year's value is computed by standardizing the annual precipitation in each of 344 climate divisions across the U.S. using the gamma distribution over the 1931-90 period. The gamma statistical distribution takes into account heavy precipitation years and extremely dry years in the historical record (in mathematical parlance, "a zero-bounded skewed distribution"). These gamma-standardized divisional values are then weighted by area and averaged to determine a national standardized value for each year.
These national values are normalized over the period of record. Negative values are drier and positive values are wetter than the mean. This index gives a more accurate indication of how precipitation across the country compares to the local normal (60-year average) climate.
The preliminary national standardized precipitation index ranked Summer 1999 also drier than the long term mean.
|
 larger image
larger image
|
larger image
|
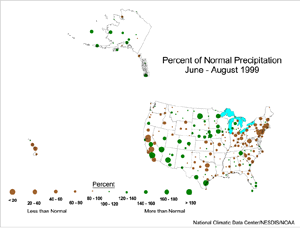
The map to the left, based on approximately 250 airport stations, shows Summer (June-August) 1999 precipitation as a percentage of 1961-1990 station normals. Widespread dryness characterized the contiguous U.S. from the southern Plains to the Northeast. The convective nature of summer thunderstorms brought spotty wetness to part of this area, while the remnants of Hurricane Bret caused heavy rains in parts of southern Texas. A band of above-normal summer precipitation stretched from the western Great Lakes to parts of the southwestern U.S.
|
The pattern in the Northwest was generally dry, with spotty wet areas. It should be noted that percent-of-normal statistics in the Southwest can sometimes be exaggerated due to the normally dry summer climate there. The Hawaiian stations indicated significant summer dryness in the Islands. The southwestern Alaskan stations were wetter than normal, but much of the rest of the state averaged near normal for Summer 1999.

 National Tornadoes
National Tornadoes
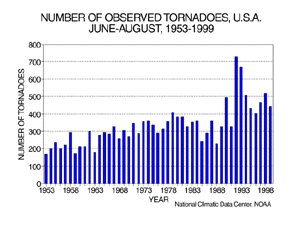
| Based on preliminary data from the National Weather Service Storm Prediction Center the count of 443 tornadoes ranked Summer (June-August) 1999 as the seventh most active summer season since 1953. The 1953-1998 average summer tornado count is 332. The summer season with the most tornadoes was 1992 with 729 while the least active summer season for tornadoes was 1953 with 166 documented tornadoes.
|
 larger image
larger image
|
It should be pointed out that the preliminary tornado count is traditionally higher than the final count and that the tornado observations have generally improved with time as better observing practices and instrumentation (especially weather radar and satellites) were utilized.

Current data are based on preliminary reports from River Forecast Center stations and First and Second Order airport stations obtained from the National Weather Service (NWS) Climate Prediction Center and real time Global Telecommunications System (GTS) monthly CLIMAT summaries. THE CURRENT DATA SHOULD BE USED WITH CAUTION. These preliminary data are useful for estimating how current anomalies compare to the historical record, however the actual values and rankings for the current year may change as the final data arrive at NCDC and are processed.
The following NCDC datasets are used for the historical U.S. data: the climate division drought database (TD-9640), and the hurricane datasets (TD-9636 and TD-9697). It should be noted that the climate division drought database consists of monthly data for 344 climate divisions in the contiguous United States. These divisional values are calculated from the 6000+ station Cooperative Observer network.



 National Tornadoes
National Tornadoes

 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information



