Sea Ice Extent
The sea ice extent data for the Arctic and Antarctic are provided by the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) and are measured from passive microwave instruments onboard NOAA Satellites. The sea ice extent period of record is from 1979–2020 for a total of 42 years.
| August 2020 | Sea Ice Extent | Anomaly 1991-2020 | Trend per decade | Rank (42 years) | Record | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| million km² | million mi² | Year(s) | million km² | million mi² | |||||
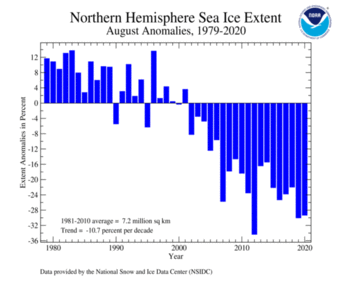
| Northern Hemisphere | 5.07 | 1.96 | -21.15% | -11.66% | Largest | 40th | 1983 | 8.19 | 3.16 |
| Smallest | 3rd | 2012 | 4.72 | 1.82 | |||||
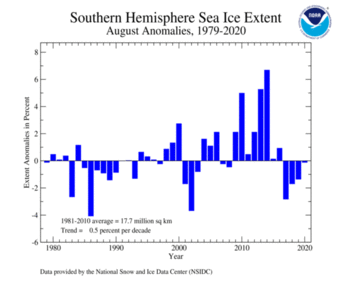
| Southern Hemisphere | 17.76 | 6.86 | -0.45% | +0.50% | Largest | 19th | 2014 | 18.91 | 7.30 |
| Smallest | 24th | 1986 | 17.00 | 6.56 | |||||
| Globe | 22.83 | 8.81 | -5.93% | -2.72% | Largest | 39th | 1982 | 25.93 | 10.01 |
| Smallest | 4th | 2019 | 22.51 | 8.69 | |||||
Data Source: National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC). Period of record: 1979–2020 (42 years)
The Northern Hemisphere sea ice extent, which is measured from passive microwave instruments onboard NOAA satellites, was 5.08 million squared km (1.96 million squared miles). This was 2.12 million square km (820,000 squared miles)—equivalent in size to the Democratic Republic of the Congo— below average. Only Augusts of 2012 and 2019 had a smaller sea ice extent. August 2020 marked the 19th consecutive August with Arctic sea ice extent below average. August 2001 was the last time the Arctic sea ice extent was above average.
The Antarctic sea ice extent during August 2020 was near average at 17.70 million squared km (6.83 million squared miles). This was also the highest August Antarctic sea ice extent since 2016.
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information