NH Snow Cover Extent
| April 2020 | Snow Cover Extent | Anomaly 1991-2020 | Trend per decade | Rank (54 years) | Record | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| million km² | million mi² | million km² | million mi² | million km² | million mi² | Year(s) | million km² | million mi² | |||
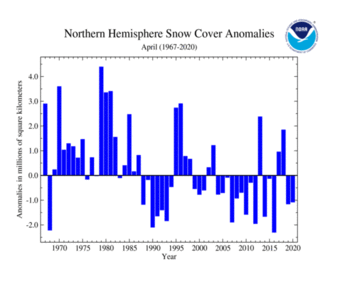
| Northern Hemisphere | 29.14 | 11.25 | -0.79 | -0.31 | -0.42 | -0.16 | Largest | 42nd | 1979 | 34.61 | 13.36 |
| Smallest | 13th | 2016 | 27.91 | 10.78 | |||||||
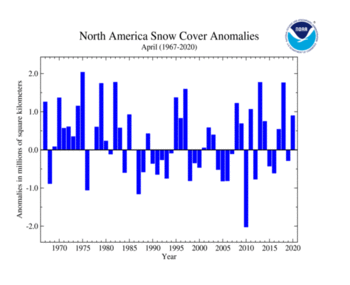
| North America | 13.94 | 5.38 | +0.77 | +0.30 | -0.07 | -0.03 | Largest | 14th | 1975 | 15.08 | 5.82 |
| Smallest | 41st | 2010 | 11.02 | 4.25 | |||||||
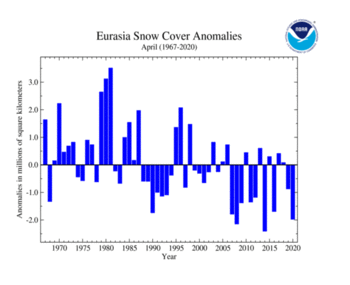
| Eurasia | 15.20 | 5.87 | -1.56 | -0.60 | -0.35 | -0.14 | Largest | 52nd | 1981 | 20.69 | 7.99 |
| Smallest | 3rd | 2014 | 14.77 | 5.70 | |||||||
Data Source: Global Snow Laboratory, Rutgers University. Period of record: 1967–2020 (54 years)
The Northern Hemisphere snow cover extent during April 2020 was 29.14 million square km (11.25 million square mi), which is 1.08 million square km (420,000 square mi) below the 1981–2010 average and the 13th smallest April extent in the 54-year record. April 2020 was characterized by unusually warm temperature across much of northern Asia and central Europe, while cooler-than-average conditions were present across much of Canada and the eastern half of the contiguous U.S.
The North American snow cover extent was above average for April at 13.94 million square km (5.38 million square mi)—the 14th largest April snow cover extent on record. Above-average snow cover extent was present across much of the southern half of Canada and the north-central tier of the contiguous U.S. Meanwhile, below-average snow cover extent was limited to parts of the northeastern and western contiguous U.S. Alaska and the contiguous U.S. April 2020 snow cover extents were near average, while Canada had slightly above-average conditions and the 15th largest April snow cover extent.
The Eurasian April snow cover extent of 15.20 million square km (5.87 million square mi) was below average and the third smallest April snow cover extent in the 54-year record. Only Aprils of 2008 and 2014 had a smaller April snow cover extent. Below-average snow cover extent was present across much of central Eurasia, with only parts of southern China and northern parts of western Russia experiencing above-average snow cover extent during April 2020.
Sea Ice Extent
The sea ice extent data for the Arctic and Antarctic are provided by the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) and are measured from passive microwave instruments onboard NOAA Satellites. The sea ice extent period of record is from 1979–2020 for a total of 42 years.
| April 2020 | Sea Ice Extent | Anomaly 1991-2020 | Trend per decade | Rank (42 years) | Record | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| million km² | million mi² | Year(s) | million km² | million mi² | |||||
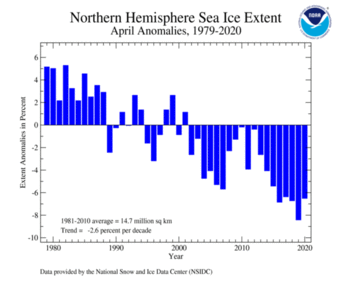
| Northern Hemisphere | 13.62 | 5.26 | -4.89% | -2.65% | Largest | 41st | 1982 | 15.47 | 5.97 |
| Smallest | 2nd | 2019 | 13.43 | 5.19 | |||||
| Southern Hemisphere | 6.66 | 2.57 | -4.17% | +1.29% | Largest | 25th | 2015 | 8.37 | 3.23 |
| Smallest | 18th | 1980 | 5.40 | 2.08 | |||||
| Globe | 20.28 | 7.83 | -4.65% | -1.36% | Largest | 36th | 1982 | 23.19 | 8.95 |
| Smallest | 7th | 2019 | 19.15 | 7.39 | |||||
Data Source: National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC). Period of record: 1979–2020 (42 years)
The Arctic sea ice extent for April 2020 was 960,000 square km (371,000 square mi) below average and the fourth smallest April extent in the 42-year record. The five smallest April snow cover extents have all occurred since 2017. April 2020 marked the 19th consecutive April with below-average sea ice extent. According to the sea ice regional analysis, the Baffin Bay, the Bering Sea, and the Sea of Okhotsk had a sea ice extent that ranked among the three smallest on record for April.
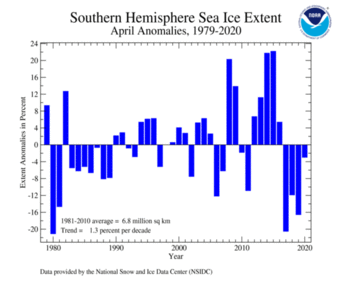
The Antarctic sea ice extent during April 2020 was slightly below average at 210,000 square km (81,100 square mi), or 3.0%, below the 1981–2010 average. This was the fourth consecutive April with sea ice extent below average. According to the NSIDC, sea ice extent was slightly below average in the Ross Sea, as well as parts of the Weddell Sea.
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information