NH Snow Cover Extent
| February 2020 | Snow Cover Extent | Anomaly 1991-2020 | Trend per decade | Rank (54 years) | Record | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| million km² | million mi² | million km² | million mi² | million km² | million mi² | Year(s) | million km² | million mi² | |||
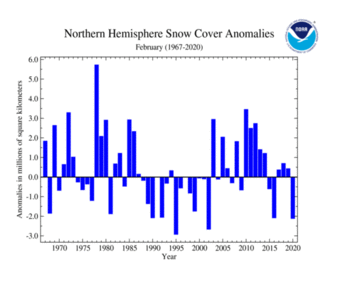
| Northern Hemisphere | 45.22 | 17.46 | -0.56 | -0.22 | -0.09 | -0.03 | Largest | 36th | 1978 | 51.32 | 19.81 |
| Smallest | 19th | 1990 | 42.16 | 16.28 | |||||||
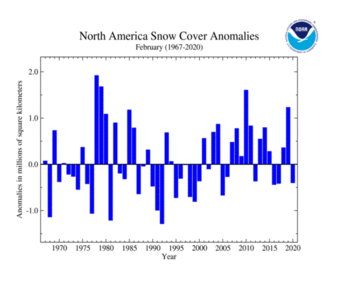
| North America | 17.39 | 6.71 | +0.18 | +0.07 | +0.07 | +0.03 | Largest | 26th | 1978 | 19.04 | 7.35 |
| Smallest | 30th | 1991 | 15.63 | 6.03 | |||||||
| Ties: 2015 | |||||||||||
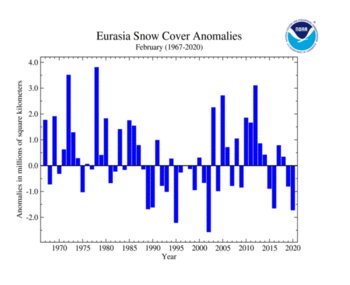
| Eurasia | 27.84 | 10.75 | -0.72 | -0.28 | -0.16 | -0.06 | Largest | 40th | 1972 | 33.26 | 12.84 |
| Smallest | 15th | 2002 | 25.91 | 10.00 | |||||||
Data Source: Global Snow Laboratory, Rutgers University. Period of record: 1967–2020 (54 years)
The Northern Hemisphere snow cover extent during February 2020 was 2.11 million square km (820,000 square miles) below the 1981–2010 average and the third smallest February snow cover extent in the 54-year period of record. Februarys of 1995 and 2002 had a smaller February snow cover extent. During February 2020, unusually warm conditions engulfed much of Europe and Asia, contributing to the small snow cover extent for the month. However, cooler-than-average temperatures were mostly present across Alaska, northern Canada, and Far East Russia.
During February 2020, the North American snow cover extent was the 16th smallest in the 54-year record at 16.72 million square km (6.45 million square miles) or 400,000 square km (160,000 square miles) below average. Above-average snow cover extent was present across parts of the northern contiguous U.S. Below-average snow cover extent was present across parts of Pacific Northwest, Great Basin, Southwest, central Plains, and Mid-Atlantic. A wet and cold winter contributed to Alaska having above-average snow cover extent during February 2020, tying with five other years as the largest snow cover extent for February. Canada and the contiguous U.S. had their 19th and 11th largest February snow cover extent, respectively, on record.
The Eurasian February snow cover extent of 26.76 million square km (10.33 million square miles) was 1.72 million square km (660,000 square miles) below average. This was also the third smallest February snow cover extent on record, trailing behind Februarys of 2002 and 1995. Above-average snow cover extent was limited to eastern Asia to the Himalayas, while below-average snow cover extent was observed across much of Europe and parts of southwestern Asia.
Sea Ice Extent
The sea ice extent data for the Arctic and Antarctic are provided by the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) and are measured from passive microwave instruments onboard NOAA Satellites. The sea ice extent period of record is from 1979–2020 for a total of 42 years.
| February 2020 | Sea Ice Extent | Anomaly 1991-2020 | Trend per decade | Rank (42 years) | Record | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| million km² | million mi² | Year(s) | million km² | million mi² | |||||
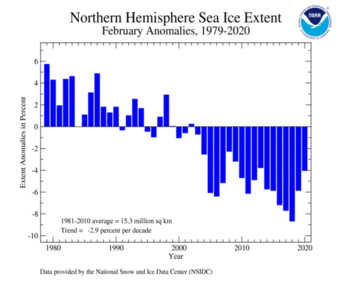
| Northern Hemisphere | 14.64 | 5.65 | -1.48% | -2.96% | Largest | 30th | 1979 | 16.18 | 6.25 |
| Smallest | 13th | 2018 | 13.97 | 5.39 | |||||
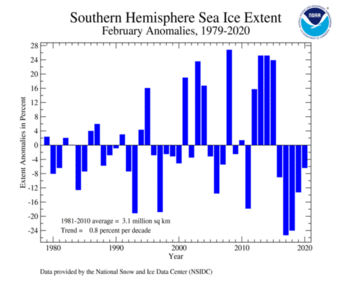
| Southern Hemisphere | 2.92 | 1.13 | -5.50% | +0.65% | Largest | 26th | 2008 | 3.89 | 1.50 |
| Smallest | 17th | 2017 | 2.29 | 0.88 | |||||
| Globe | 17.56 | 6.78 | -2.17% | -2.28% | Largest | 34th | 1979 | 19.32 | 7.46 |
| Smallest | 9th | 2018 | 16.30 | 6.29 | |||||
Data Source: National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC). Period of record: 1979–2020 (42 years)
Arctic daily sea ice growth during February 2020 was near the 1981–2010 average. Overall, the February average Arctic sea ice extent of 14.68 million square km (5.67 million square miles) was 620,000 square km (240,000 square miles), or 4.0 percent, below the 1981–2010 average and the 13th smallest February extent in the 42-year record, according to analysis by the National Snow and Ice Data Center using data from NOAA and NASA. February 2020 also marked the 18th consecutive February with below-average sea ice extent. Although the sea ice extent was below average, compared to recent Februarys, February 2020 had the largest sea ice extent since 2013. Regionally, below-average February sea ice extent was present across parts of the Barents and Kara Seas and eastern Greenland Sea.
Antarctic sea ice extent during February was 2.87 million square km (1.11 million square miles), which is 200,000 square km (80,000 square miles), or 6.5 percent, below the 1981–2010 average. This value tied with February 1981 as the 13th smallest February sea ice extent on record. February 2020 marked the fifth consecutive February where sea ice extent has been below average for the Antarctic. According to NSIDC, the Antarctic sea ice extent likely reached its annual minimum on February 20 and 21 at 2.69 million square km (1.04 million square miles), which is near the 1981–2010 median.
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information