Sea Ice Extent
| June 2019 | Sea Ice Extent | Anomaly 1991-2020 | Trend per decade | Rank (41 years) | Record | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| million km² | million mi² | Year(s) | million km² | million mi² | |||||
| Northern Hemisphere | 10.59 | 4.09 | -6.28% | -4.07% | Largest | 40th | 1979 | 12.53 | 4.84 |
| Smallest | 2nd | 2016 | 10.41 | 4.02 | |||||
| Ties: 2010 | |||||||||
| Southern Hemisphere | 12.25 | 4.73 | -8.99% | +0.82% | Largest | 41st | 2014 | 14.69 | 5.67 |
| Smallest | 1st | 2019 | 12.25 | 4.73 | |||||
| Globe | 22.84 | 8.82 | -7.75% | -1.41% | Largest | 41st | 1979 | 26.72 | 10.32 |
| Smallest | 1st | 2019 | 22.84 | 8.82 | |||||
Data Source: National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC). Period of record: 1979–2019 (41 years)
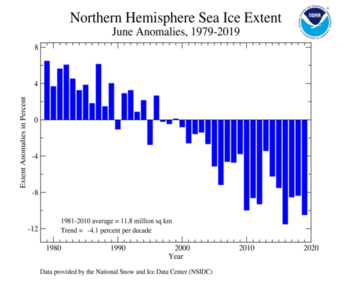
The Arctic (Northern Hemisphere) sea ice extent—which is measured from passive microwave instruments onboard NOAA Satellites— averaged for June 2019 was 10.53 million square km (4.07 million square miles), which is 1.23 million square km (475,000 square miles) or 10.5% below average. This was the Arctic's second lowest June sea ice extent, trailing behind the record set in June 2016 by 120,000 square km (46,300 square miles). June 2019 also marks the 20th consecutive June with Arctic sea ice extent below average. According to the National Snow and Ice Data Center, sea ice extent was well below average on the Pacific side of the Arctic and open waters across the Bering Strait and the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas as well in Melville Island (Canadian Arctic Archipelago).
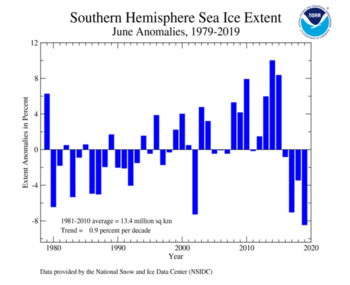
June 2019 marks the fourth consecutive June that the Antarctic (Southern Hemisphere) sea ice extent was below average at 1.1 million square km (425,000 square miles) or 8.5% below the 1981–2010 average. This was the smallest June extent in the 41-year record, surpassing the previous record set in 2002 by 160,000 square km (62,000 square miles).
For further information on the Northern and Southern Hemisphere snow and ice conditions, please visit the NSIDC News page.
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information