NH Snow Cover Extent
| April 2015 | Snow Cover Extent | Anomaly 1991-2020 | Trend per decade | Rank (49 years) | Record | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| million km² | million mi² | million km² | million mi² | million km² | million mi² | Year(s) | million km² | million mi² | |||
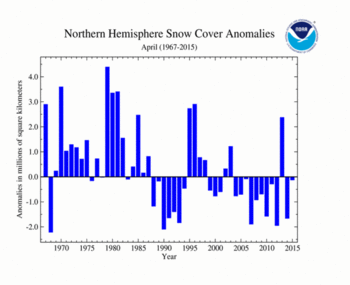
| Northern Hemisphere | 30.09 | 11.62 | +0.16 | +0.06 | -0.48 | -0.19 | Largest | 28th | 1979 | 34.61 | 13.36 |
| Smallest | 22nd | 1968 | 28.00 | 10.81 | |||||||
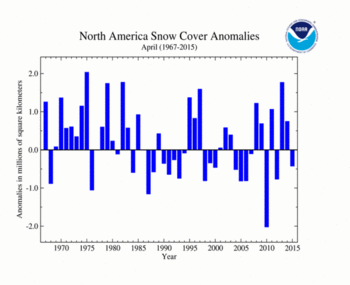
| North America | 12.62 | 4.87 | -0.55 | -0.21 | -0.12 | -0.05 | Largest | 35th | 1975 | 15.08 | 5.82 |
| Smallest | 15th | 2010 | 11.02 | 4.25 | |||||||
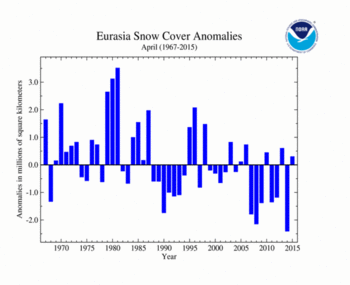
| Eurasia | 17.47 | 6.75 | +0.71 | +0.27 | -0.35 | -0.14 | Largest | 21st | 1981 | 20.69 | 7.99 |
| Smallest | 29th | 2014 | 14.77 | 5.70 | |||||||
Data Source: Global Snow Laboratory, Rutgers University. Period of record: 1967–2015 (49 years)
During April 2015, the Northern Hemisphere snow cover extent (SCE) was 30.09 million square km (11.62 million square miles), 130,000 square km (50,000 square miles) below the 1981-2010 average. This was the 22nd smallest (28th largest) April SCE in the 49-year period of record for the Northern Hemisphere. Eurasia's April SCE was above average, while North America's was below average.
The April North American SCE was 12.62 million square km (4.87 million square miles), 420,000 square km (160,000 square miles) below average and the 15th smallest (35th largest) on record. For April, the contiguous U.S. SCE was the ninth smallest on record; Alaska's SCE was the seventh smallest on record; and Canada's SCE was the 16th smallest average. Below-average snow cover was observed across the western two-thirds of North America. Above-average snow cover was observed across parts of eastern Canada and the northeastern United States.
The Eurasian SCE during April was 17.47 million square km (6.75 million square miles), 300,000 square km (120,000 square miles) above average. This was the 21st largest (29th smallest) April SCE on record for Eurasia. Below-average snow cover was observed across northern Europe and parts of central Russia. Above-average snow cover was observed across far eastern Asia, the Tibetan Plateau, and the Himalayas.
Sea Ice Extent
| April 2015 | Sea Ice Extent | Anomaly 1991-2020 | Trend per decade | Rank (37 years) | Record | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| million km² | million mi² | Year(s) | million km² | million mi² | |||||
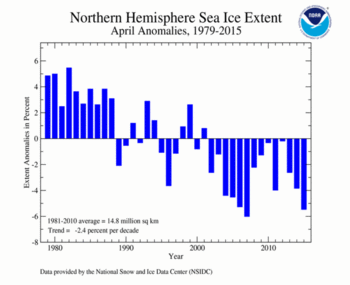
| Northern Hemisphere | 13.89 | 5.36 | -3.00% | -2.37% | Largest | 36th | 1982 | 15.47 | 5.97 |
| Smallest | 2nd | 2007 | 13.85 | 5.35 | |||||
| Southern Hemisphere | 8.37 | 3.23 | +20.43% | +4.03% | Largest | 1st | 2015 | 8.37 | 3.23 |
| Smallest | 37th | 1980 | 5.40 | 2.08 | |||||
| Globe | 22.26 | 8.59 | +4.65% | -0.28% | Largest | 6th | 1982 | 23.19 | 8.95 |
| Smallest | 32nd | 2006 | 19.92 | 7.69 | |||||
Data Source: National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC). Period of record: 1979–2015 (37 years)
According to the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), the Northern Hemisphere sea ice extent — which is measured from passive microwave instruments onboard NOAA satellites — averaged for April 2015 was 13.96 million square km (5.39 million square miles), 810,000 square km (310,000 square miles), or 5.48 percent, below the 1981-2010 average. This was the second smallest April Arctic sea ice extent on record, at 80,000 square km (30,000 square miles) larger than the record small April sea ice extent that occurred in 2007. Sea ice extent rapidly declined early in the month, slowed mid-month, and picked up momentum towards the end of the month. When averaged for April, sea ice extent was below average in the Barents Sea, the Sea of Okhotsk, and the Bering Sea. Sea ice was above average off the Newfoundland coast, in the Davis Strait, and in the Labrador Sea. For April, the Arctic sea ice extent is decreasing at an average rate of 2.4 percent per decade.
The April 2015 Southern Hemisphere sea ice extent was 9.06 million square km (3.50 million square miles), 1.66 million square km (640,000 square miles), or 22.43 percent, above the 1981-2010 average. This was the largest April Antarctic sea ice extent on record. The previous record large April Antarctic sea ice extent occurred in 2014 and was 30,000 square km (10,000 square miles) smaller than the April 2015 extent. Above-average sea ice was observed in the Weddell and Ross Seas. Antarctic sea ice extent during April is increasing at an average rate of 3.9 percent per decade.
When combining the Northern and Southern Hemisphere sea ice extents, the globally-averaged sea ice extent during April was 23.02 million square km (8.89 million square miles), 3.8 percent above the 1981-2010 average. This was the fifth largest April global sea ice extent on record. Global sea ice extent during April is decreasing at an average rate of 0.2 percent per decade.
For further information on the Northern and Southern Hemisphere snow and ice conditions, please visit the NSIDC News page.
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information