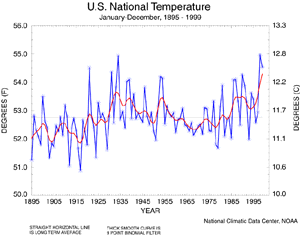
 U.S. National Temperature - 1999 Annual
U.S. National Temperature - 1999 Annual
For the calendar year 1999, the United States experienced its third warmest year since 1895 with a preliminary average value for 1999 of 54.5 degrees F. This follows 1998's all time record of 54.9 degrees. Both years' values exceed those experienced during the warm decade of the 1930s. Similar to the global temperature trend, 1999 continues a trend toward long-term warming in the U.S.(0.5 degrees C per Century) with much of the warming occurring during the two periods 1910-45 and 1976-present.
| This annual temperature time
series graph is based on NCDC's U.S. Historical Climatology Network, a high-quality moderate sized data set of monthly averaged maximum, minimum, and mean temperature and total monthly precipitation developed to assist in the detection of regional climate change. The annual temperature values for each year from 1900 to 1999 are available.
|
larger image
|
larger image
|
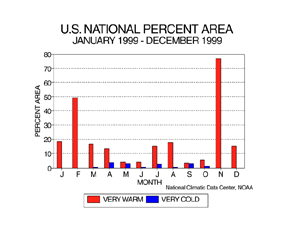
Much of the year was characterized by unusually warm monthly temperatures. Three-fourths of the contiguous U.S. experienced very warm conditions in November 1999, and nearly half of the contiguous U.S. was very warm in February. Six of the months had between 10 and 20 percent of the country much warmer than normal. A few areas (less than 5 percent in any given month) had much colder than normal monthly mean temperatures from March to October.
|
| The map animation provided to the right shows the geographical pattern of temperature anomalies for the last 12 months, compared to a base period of 1931-1990.
|
animated image
|

 U.S. National Precipitation - 1999 Annual
U.S. National Precipitation - 1999 Annual
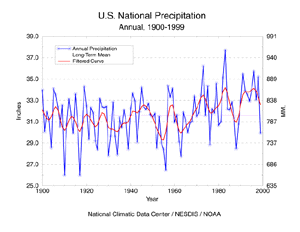
larger image
|
Preliminary data for 1999 indicate that the United States had the 22nd driest year out of the last 100 years, with nationally averaged precipitation of 29.93". This annual precipitation time series graph is based on NCDC's U.S. Historical Climatology Network, a high-quality moderate sized data set of monthly averaged maximum, minimum, and mean temperature and total monthly precipitation developed to assist in the detection of regional climate change. The annual precipitation values for each year from 1900 to 1999 can be seen here.
|
Although the national annual precipitation value was not extreme, there were significant spatial and temporal variations during 1999. The year began on a wet note in the eastern portion of the U.S., with nearly a fourth of the contiguous U.S. unusually wet in January and nearly a third unusually wet in April. Dry conditions also developed early in the year, with a fifth of the country very dry in February. The dry regime that became established by April led to record setting growing season dryness throughout the Ohio Valley and Northeast. The drought was followed by record setting rainfall as two hurricanes traversed the eastern seaboard in September. States from North Carolina to Maine experienced a record or near record wet September and numerous location reported their heaviest 24-hour precipitation, wettest September or wettest any month on record.
| The warm season months July to September were characterized by a balancing act between unusual wetness and unusual dryness, with a tenth or more of the country each experiencing very wet or very dry conditions. The last four months of 1999 were dominated by unusual dryness, with November having more than a third of the country very dry.
|
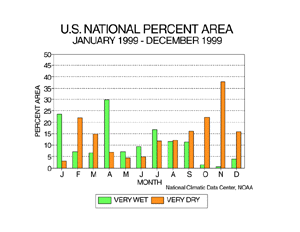
larger image
|
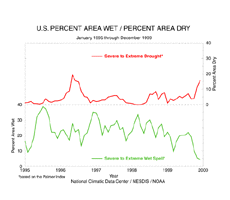
larger image
|
Long-term drought areal coverage (as measured by the Palmer Drought Index) continued to increase, with December 1999 having about 16% of the country in severe to extreme drought. The percent area of the country experiencing severe to extreme wetness dropped to about four percent.
|

 Tornadoes - 1999 Annual
Tornadoes - 1999 Annual
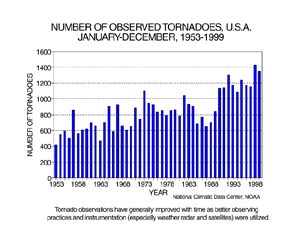
larger image
|
The preliminary annual count of tornadoes for 1999 is 1351. This compares to a 1953-1998 average of 837, a maximum of 1424 last year, and a minimum in the 47-year record of 421, which occurred in 1953.
|
It should be noted that the preliminary tornado count is traditionally higher than the final count and that the tornado observations have generally improved with time as better observing practices and instrumentation (especially weather radar and satellites) were utilized.

 U.S. National Temperature - December 1999
U.S. National Temperature - December 1999
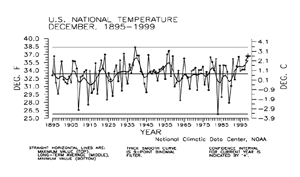
larger image
|
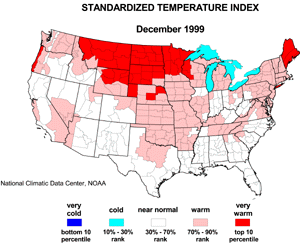
Preliminary date for December 1999 indicated that the monthly mean temperature averaged across the contiguous United States was the 11th warmest such month since 1895. About 15% of the country was much warmer than normal while near zero percent was much cooler than normal.
|
| The preliminary December national standardized temperature index ranked December 1999 as the seventh warmest December since records began in 1895.
|
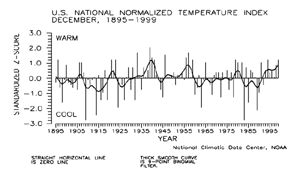
larger image
|
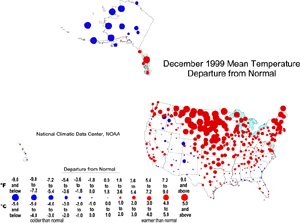
larger image
|
The map to the left, based on approximately 250 airport stations, shows departures from the 1961-1990 normal of average temperatures for December 1999. Much of the contiguous U.S. averaged above normal, with the warmest departures occurring from the northern Rockies to the central and northern Plains states and in the Northeast. Below normal monthly temperatures occurred over parts of the Southeast and Far West. Stations in the southeastern Alaskan panhandle averaged warmer than normal in December while the rest of the state was colder than normal. The Hawaiian stations averaged near normal.
|
| The December temperature variability map over the contiguous U.S. is shown to the right. Day-to-day variability in mean temperature was below normal over most of the country, with the greatest departures occurring over the Northwest, central and southern Plains, and northern Maine. Many of these areas experienced unusually warm--and persistently warm--weather during December. Day-to-day temperature variability was higher than normal across much of interior Alaska to the Aleutian island chain. Variability at the Hawaiian stations was mixed, but near normal.
|
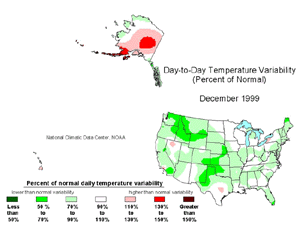
larger image
|

 U.S. National Precipitation - December 1999
U.S. National Precipitation - December 1999
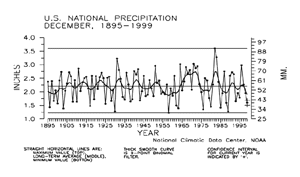
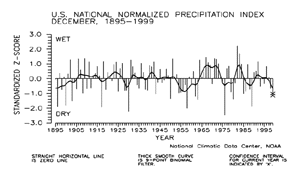
| Based upon preliminary precipitation date, December 1999 ranked as the 15th driest such month since 1895. Nearly 16% of the country was much drier than normal while about four percent of the country was much wetter than normal.
|
larger image
|
larger image
|
The preliminary December national standardized precipitation index ranked December 1999 as the 13th driest December since records began in 1895.
|
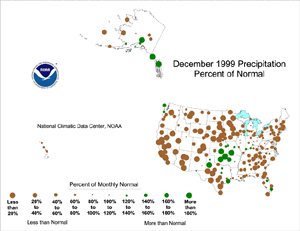
| Like November, most of the U.S. (including many of the stations in Alaska and Hawaii) was drier than normal during December 1999. Above-normal precipitation fell along the Northwest coast, the central Plains and scattered areas to the east and south, and in southeastern and south central Alaska. But the watchwords for the nation in December was: STILL DRY!
|
larger image
|
The map immediately above, based on approximately 250 airport stations, shows December 1999 total precipitation as a departure from 1961-1990 station normals.

Current data are based on preliminary reports from River Forecast Center stations and First and Second Order airport stations obtained from the National Weather Service (NWS) Climate Prediction Center and real time Global Telecommunications System (GTS) monthly CLIMAT summaries. THE CURRENT DATA SHOULD BE USED WITH CAUTION. These preliminary data are useful for estimating how current anomalies compare to the historical record, however the actual values and rankings for the current year may change as the final data arrive at NCDC and are processed.
The following NCDC datasets are used for the historical U.S. data: the climate division drought database (TD-9640), and the hurricane datasets (TD-9636 and TD-9697). It should be noted that the climate division drought database consists of monthly data for 344 climate divisions in the contiguous United States. These divisional values are calculated from the 6000+ station Cooperative Observer network.

 U.S. National Temperature - 1999 Annual
U.S. National Temperature - 1999 Annual
 U.S. National Precipitation - 1999 Annual
U.S. National Precipitation - 1999 Annual
 Tornadoes - 1999 Annual
Tornadoes - 1999 Annual
 U.S. National Temperature - December 1999
U.S. National Temperature - December 1999
 U.S. National Precipitation - December 1999
U.S. National Precipitation - December 1999
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information












