Global Hazards and Significant Events
September 2008
Hurricanes Gustav, Hanna, and Ike brought widespread floods across the Caribbean and the U.S. Additional information can be found below.

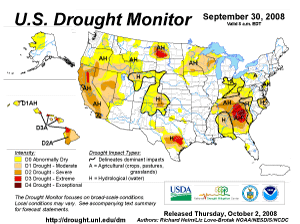
Moderate to extreme drought conditions continued across parts of the Hawaiian Islands, the western, central, and southeastern parts of the continental U.S. Exceptional drought persisted across western South Carolina. As of September 30, 29% of the western U.S., 17% of the South, 13% of the High Plains, 42% of the Southeast, and 24% of the contiguous U.S. were in moderate to exceptional drought, according to the U.S. Drought Monitor. For a complete drought analysis across the United States, please see the U.S. drought page.
High temperatures and strong winds were conducive to the development of wildfires across southern Africa during the first week of September. The wildfires affected Mozambique, South Africa, and Swaziland, killing hundreds of livestock, affecting over 3,000 residents, and claiming the lives of 89 people — 49 people in central Mozambique and 40 in South Africa and Swaziland (Associated Press/BBC News).
According to the Australian Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne had the driest September since records began in 1855, with a total of 12 mm (0.47 inch) of rain. The previous record was set in 1907 when a total of 13.4 mm (0.53 inch) of rain fell.
In Szeged, Hungary, a new daily maximum temperature record was set on September 7 when temperatures rose to 37.6°C (100°F), surpassing the previous record of 36.7°C (98°F) set in 1946 (BBC News).

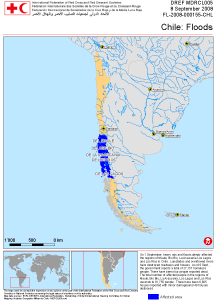
Heavy rain fell across southern Chile on August 31 - September 1. The heavy downpours triggered floods and landslides that affected more than 81,700 people, killed four people, and destroyed or damaged nearly 10,900 houses (IFRC). According to reports, the rains were the heaviest in nearly four decades (Associated Press).
Intense rains on the 7th caused flooding and mudslides in Penang, Malaysia. More than 10,000 people were forced to evacuate the affected area. No fatalities were reported (BBC News).
Storms brought flooding and mudslides during the 6th-8th to areas of the United Kingdom, where torrential rain caused rivers to overflow their banks and roads to be inundated. It was reported that hundreds of people were forced to evacuate after nearly 1,000 properties were flooded in the town of Morpeth. Six fatalities were reported (Associated Press).
Flash floods caused by heavy rain on September 10-11 killed 16 people and forced hundreds of people to leave their homes across northern Iraq and parts of Iran. According to reports, the floods destroyed several hydroelectric generators in Iran's Choman district (BBC News).
Incessant rains produced by a tropical disturbance affected Puerto Rico on September 20-24. According to a local newspaper, the tropical disturbance dumped as much as 660 mm (26 inches) of rain in a period of 24 hours. This amount of rain surpassed the previous record of 603.2 mm (23.75 inches) set on October 1985 (El Nuevo Día). The southern portion of the island experienced the heaviest rainfall, prompting landslides and many rivers to overflow their banks that flooded hundreds of homes (Reuters). According to the USGS, the Gurabo River's gage height rose 7.62 m (25 feet) in less than 24 hours on September 21, peaking at 9.23 m (30.29 feet). Many homes were damaged or destroyed and four fatalities were attributed to the floods. The heavy rain reportedly caused Puerto Rico's agricultural industry at least $14 million in losses. The hardest hit crops were coffee and bananas (Associated Press). It was reported that president George W. Bush declared eight municipalities disaster zones (El Nuevo Día).
In southeastern Mexico, heavy rain caused rivers to be well above flood stage, flooding thousands of homes and forcing hundreds of people to evacuate the area. Five fatalities were blamed on the heavy rain (Associated Press).
Torrential rain affected nearly 700,000 people across parts of Thailand on September 22-24. The heavy downpours caused severe flooding, damaging nearly 1,900 houses and tens of thousands of acres of farmland. It was reported that the floods claimed the lives of 16 people (AFP).
In southwest China, heavy rain triggered flash floods and landslides in the Sichuan province on September 24, killing 14 people and leaving 40 others missing. According to reports, more than 42,000 houses were destroyed (Associated Press).
Heavy monsoon-related rainfall drenched parts of India during September, triggering floods and mudslides and causing damage to crops and property. The heavy downpours prompted rivers to breach their banks, producing widespread floods in eastern Orissa that affected nearly 2.4 million people. According to reports, this was the worst monsoon flooding in the state in 26 years (Associated Press). The floods were blamed for the death of 173 people across India (AFP).

No reports of significant severe storms were received during September 2008.

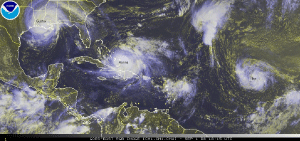
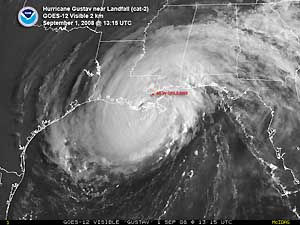
Hurricane Gustav, which developed during the last week of August, pounded several Caribbean nations before making landfall west of Grand Isle, LA on September 1 as a category 3 hurricane with maximum sustained winds near 185 km/hr (115 mph or 100 knots). Nearly two million people fled coastal areas as many feared a repetition of Hurricane Katrina in 2005. According to reports, this was described as the biggest evacuation in U.S. history (AFP). Gustav's ferocious winds brought down trees and power lines, leaving thousands of customers without power in Louisiana (Associated Press). As Gustav moved inland, the storm weakened to a depression. The storm was blamed for 25 fatalities in the U.S.
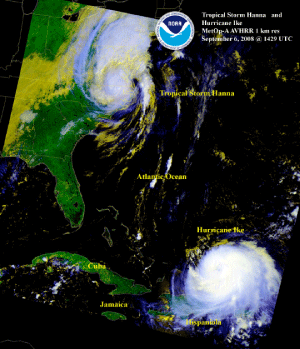
Hurricane Hanna developed as a tropical depression in the Atlantic Ocean on August 28, strengthening into a tropical storm later that day. By September 1, Hanna intensified to a hurricane with maximum sustained winds near 130 km/hr (81 mph or 70 knots) as it tracked towards the Bahamas. Although Hanna did not make landfall on the Island of Hispaniola, the storm's outer rain bands brought heavy rain to Haiti's saturated ground. The copious rain caused fatal floods and mudslides, claiming the lives of 529 people (Reuters) and destroying immense areas of crops (BBC News). The worst affected city was Gonaïves, which according to reports was completely devastated (BBC News). The storm tracked towards the Eastern Seaboard, making landfall near the North and South Carolina border on the 6th with maximum sustained winds near 93 km/hr (58 mph or 50 knots). Hanna brought much needed rain to the Carolinas, however severe to exceptional drought persisted according to the 9 September 2008 U.S. Drought Monitor Map. The storm moved towards the Northeast region, dumping heavy rains and lashing the region with strong winds. Hanna was blamed for flooding highways, delaying flights, and leaving thousands of residents without power (Associated Press).
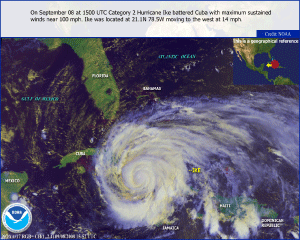
Hurricane Ike developed as a tropical storm, west of the Cape Verde Islands, on September 1. The storm quickly intensified, reaching its peak strength (a dangerous Category 4 hurricane) on the 4th when it had maximum sustained winds near 233 km/hr (145 mph or 126 knots) and a pressure of 935 mb. So far, Ike is the strongest storm in the 2008 Atlantic hurricane season. Haiti, already ravaged by three previous tropical storms (Fay, Gustav, and Hanna), was affected by Ike's outer rain bands. Torrential rain fell, producing swollen rivers, mudslides, and floods, which claimed the lives of 74 people (AFP). The storm tracked towards Cuba (also previously affected by Fay, Gustav, and Hanna), which was preparing itself for a fourth time, evacuating nearly a million Cubans across the coastal areas. Prior to making landfall in Cuba, Ike slightly weakened to a Category 3 hurricane. Ike made landfall in eastern Cuba on September 7 with maximum sustained winds near 193 km/hr (120 mph or 104 knots). Ike's ferocious winds tore off roofs, toppled trees and power lines. As the storm roared across the island, Ike weakened, however, it remained a dangerous Category 1 hurricane. The storm crossed over western Cuba, striking the area with additional flooding and storm surge (AFP). Hurricane Ike was responsible for seven fatalities in Cuba, the highest death toll for any storm in years, according to reports. Ike's death toll in Cuba exceeds the death toll from Hurricane Michelle in 2001 when five fatalities were reported (Associated Press). It has been reported that Hurricane Gustav and Ike caused nearly 5 billion U.S. dollars in damages. More than 63,000 homes were destroyed and about 450,000 were damaged (Associated Press).
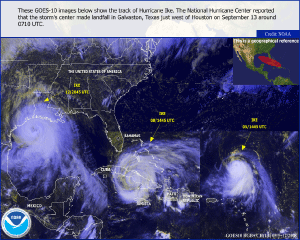
After lashing Cuba, Ike moved into the Gulf's warm waters, tracking towards the U.S.-Mexico coasts. As the storm moved steadily towards the Texas coast, Ike strengthened into a Category 2 hurricane. Ike was a large storm. Long before it made landfall, the Louisiana and Texas coast and the Florida Keys felt Ike's effects. The storm made U.S. landfall at Galveston, Texas on the 13th with maximum sustained winds near 176 km/hr (109 mph or 95 knots). Ike brought widespread floods across the Galveston area. Houston was also pummeled as the storm moved inland, blowing out windows and leaving millions of residents without power (BBC News). As the storm tracked towards the Midwest, it weakened. However, Ike's remnants caused havoc across the Midwest. Torrential rain and strong winds were responsible for inundating homes and causing blackouts to more than a million homes and businesses. The storm dumped 152-203 mm (6-8 inches) of rain across parts of Indiana, Illinois, and Missouri. The storm was also responsible for spawning a tornado in Arkansas that damaged several buildings. Ike was blamed for 15 fatalities across the Midwest, which brought the U.S. death toll from Ike to nearly 40 (Associated Press).
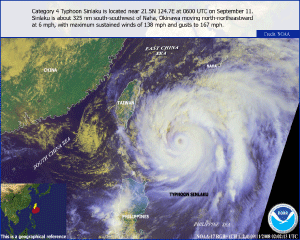
Typhoon Sinlaku developed as a tropical depression in the western Pacific Ocean, east of the northern Philippine Islands, on September 8 and became a tropical storm later that same day. Although the storm did not make landfall in the Philippines, Sinlaku's effects were felt across the island of Luzon, Philippines. The storm's rainbands prompted heavy downpours that quickly flooded the streets and homes on the 8th. By the 9th, Sinlaku strengthened to a typhoon but reached its peak intensity on the 10th with maximum sustained winds near 231 km/hr (144 mph or 125 knots). The typhoon moved towards the northeastern coast of Taiwan where it made landfall on the 14th with maximum sustained winds near 148 km/hr (92 mph or 80 knots). Sinlaku lashed the island with strong winds and heavy downpours. The typhoon was blamed for four fatalities and for leaving seven other people missing in central Taiwan. According to reports, Sinlaku dumped more than 1,016 mm (40 inches) of rain in the mountainous regions, causing deadly mudslides and the overflow of rivers that forced hundreds of people to evacuate the affected areas (Associated Press/Reuters). Sinlaku weakened to a tropical storm as it exited Taiwan, tracking towards Japan. The storm briefly intensified to a typhoon but weakened once again before making landfall in southern Kyushu on September 18 with maximum sustained winds near 139 km/hr (86 mph or 75 knots). The storm produced flooding and triggered several mudslides in Kagoshima. However, no fatalities were reported (BBC News).
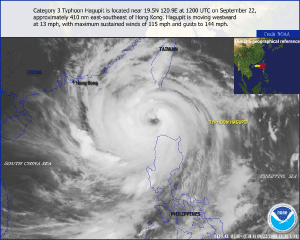
Typhoon Hagupit developed as a tropical depression in the western Pacific Ocean on the 18th. The storm reached tropical storm strength on the 19th and attained typhoon status on the 21st. The typhoon's outer rainband affected Taiwan and northern Philippine as it moved across the Luzon Strait towards southeastern China. Hagupit was blamed for the deaths of three people and for trapping 13 others in a gold mine in the Philippines (Reuters). On September 23, Hagupit reached its peak intensity with maximum sustained winds near 222 km/hr (138 mph or 120 knots) as it moved across the South China Sea. The typhoon made landfall in the province of Guangdong on the 24th with maximum sustained winds near 195 km/hr (121 mph or 105 knots). The storm brought torrential rain and ferocious winds which killed ten people, destroyed nearly 18,500 houses, flooded more than 800 homes, and destroyed crops. According to reports, economic losses due to the typhoon are estimated to be 923.7 million U.S. dollars (AFP). It was reported that Hagupit was the worst typhoon to hit the Guangdong province in a decade (BBC News). As the typhoon moved further inland, towards Vietnam, it began to weaken. However, Hagupit brought torrential downpours to northern Vietnam, triggering fatal floods and landslides. The storm was responsible for destroying thousands of hectares of crops, inundating several thousand homes, and claiming the lives of 41 people (AFP). In Vietnam, the economic losses were estimated to be at least 65 million U.S. dollars (Associated Press).
Hurricane Kyle developed as a tropical disturbance that moved over Puerto Rico, causing widespread floods that claimed the lives of four people. By the 24th the disturbance exited the Caribbean as it tracked northward. The disturbance attained tropical storm strength on the 25th and strengthened into a hurricane on September 27. The storm reached its peak intensity with maximum sustained winds near 120 km/hr (75 mph or 65 knots) before making landfall in Nova Scotia on the 28th. According to reports, 12,000 power outages were reported along the south shore (Associated Press). Kyle weakened immediately after landfall.
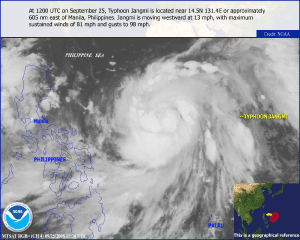
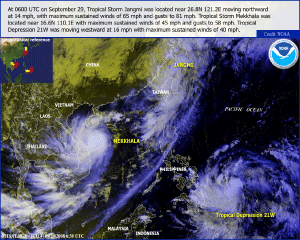
Typhoon Jangmi developed in the northwestern Pacific Ocean as a tropical depression on the 23rd. By September 25, Jangmi attained typhoon status, but reached its peak intensity with maximum sustained winds near 250 km/hr (155 mph or 135 knots) on the 27th. Jangmi made landfall in Taiwan on September 28, becoming the most powerful typhoon to hit the island during the 2008 season. It was reported that Jangmi dumped as much as 1,124 mm (44 inches) of rain on some parts of the island (Reuters) and left nearly 86,000 households without power. Two fatalities were reported (Associated Press). The storm weakened as it moved across Taiwan and was downgraded to a tropical storm on the 29th as it exited Taiwan and headed towards Japan. The storm became extratropical on the 30th.
Tropical Storm Mekkhala developed as a tropical depression in the South China Sea on September 28. The next day the depression strengthened to a tropical storm and on the 30th made landfall in central Vietnam. The storm pounded the country with maximum sustained winds near 88 km/hr (55 mph or 48 knots) and heavy rain (BBC News), blowing off tin roofs and downing trees and electric poles. According to reports, eight fatalities were reported with eight others missing (Associated Press).
For 2008 basin tropical cyclone statistics, please refer to the following:
Australian Basin
North Indian Ocean Basin
Western North Pacific Basin
South Pacific Basin
South Indian Ocean Basin
Northeast Pacific Ocean Basin
Atlantic Basin

No reports of significant extratropical cyclones were received during September 2008.

A new national daily record was set for Hungary on September 15 when the city of Sopron recorded its coldest temperature of 8.6°C (47°F). The previous record was set in Zalaegerszeg in 1925 when temperatures only reached 10.5°C (51°F) (BBC News).
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information