 Cyclone Glenda |
March 2006 Tropical Cyclone Glenda made landfall in Western Australia on March 30. It was the second cyclone to strike Australia in as many weeks. Additional information can be found below. |

Across the United States, significant drought extended from the Desert Southwest eastward through the Southern Plains. Exceptional drought classification was noted across Deep South Texas. |
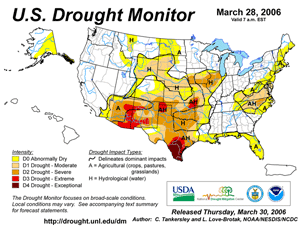 U.S. Drought Monitor |
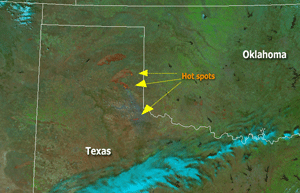 Texas Wildfires |
Severe wildfires/grassfires charred more than 340,000 hectares (840,000 acres) in Texas, killing 11 people and approximately 10,000 cattle and horses (Associated Press). |
The biggest fires were located in the Texas Panhandle, with Gray and Hutchinson counties among the hardest-hit. Other significant fire activity was reported in Oklahoma by the 16th. |
 Wildfires Affect Gray County, Texas |
 African Weather Assessment |
A severe long-term drought continued throughout areas of Ethiopia, Somalia and Kenya. In Kenya, an estimated 3.5 million people were in need of food aid (Associated Press). Rainfall during the first week of March in Kenya did little to alleviate long-term dryness. In southern Somalia, nearly 2.1 million people were in need of critical food assistance as the drought was characterized as the worst in ten years. Similarly, nearly 2 million people in neighboring southern Ethiopia were in urgent need of food assistance due to drought (OCHA). For the latest African analysis and forecast, see the Famine Early Warning System Network. |

Heavy rain/thunderstorms and strong winds occurred in areas of Peru during late February and early March 2006. By early March, over 65 houses had been destroyed displacing an estimated 325 people in northern Peru's Tumbes department. In the southern part of the country, additional flooding and mudslides were reported (IFRC). |
 Peru Flooding |
Across central and southern Malawi, heavy rainfall in early March produced flooding that left 8,000 people homeless. The floods occurred in the country's prime tourist district located in the southern Mangochi region. Flooding in the Mangochi district was reportedly the worst in 28 years (Associated Press). |
In Australia, heavy rainfall along the east coast stranded thousands of people on the 3rd. Around 2,500 residents of the city of Bellingen in northern New South Wales were temporarily isolated by river flooding (AFP). |
Exceptionally heavy rain since February 2006 in Hawaii caused flooding and a dam failure in Kilauea on the 14th, forcing the release of around 1.1 million cubic meters (300 million gallons) of water. There were at least two fatalities and seven reported missing (CNN). |
In Ecuador, heavy rainfall which began in February 2006 continued into the first week of March through coastal sections of the country. Over 11,000 families totaling over 50,000 people were severely affected by flooding. There were nine reported fatalities (OCHA). |


In Bangladesh, a severe thunderstorm produced a deadly tornado that affected six villages of Bagerhat District in the southern part of the country on the 4th. The tornado destroyed approximately 500 dwellings and uprooted hundreds of trees. More than 500 families were affected, with 4 deaths and more than 50 injuries reported (IFRC). |
In the Democractic Republic of Congo (DRC), a severe thunderstorm produced a possible tornado that impacted the town of Oicha. There were 3 confirmed deaths and 66 injuries, and more than 1,000 building sustained damage (OCHA). |
Severe weather affected parts of the U.S. Southern Plains and Midwest, with over 100 reported tornadoes in 5 states from Oklahoma to Illinois during the 11th-13th. There were 10 fatalities (AFP). |
 Severe Weather Reports March 10-13 |
In Germany, two people were killed and 80,000 homes suffered power outages when a tornado struck the northern city of Hamburg late on the 27th. The storm ripped off roofs and overturned several cars. Around 300,000 people in Hamburg spent the night without electricity (AFP). |


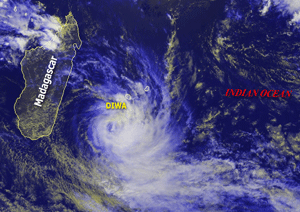 Tropical Cyclone Diwa |
Tropical Cyclone Diwa developed in the south Indian Ocean east of Madagascar on the 4th, passing approximately 230 km (140 miles) to the west of Reunion Island (France) on the 5th. Heavy rainfall and winds gusting as high as 120 km/hr (65 knots or 75 mph) occurred on the island, producing power outages to 10,000 homes and water utilities interruptions to 20,000 (AFP). |
Tropical Cyclone Larry developed in the Coral Sea on the 18th, reaching Australia's Queensland coast just south of Cairns near Innisfail on the 20th. Maximum sustained winds at the time of landfall were at least 185 km/hr (100 knots or 115 mph) with gusts as high as 290 km/hr (155 knots or 180 mph). While there were no fatalities, there were 30 injuries with damage to over 55 percent of the homes in Innisfail (Associated Press). The cyclone was described as one of the most powerful cyclones to hit Australia in decades, wiping out nearly 90 percent of the banana crop in the center of Australia's banana production region (Reuters). |
 Cyclone Larry |
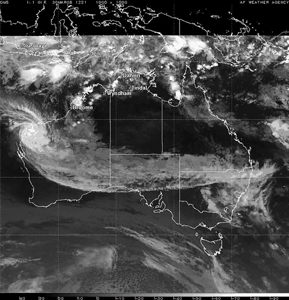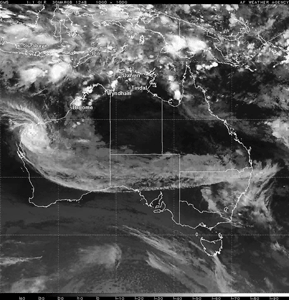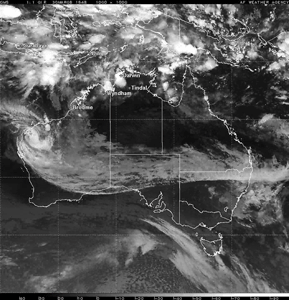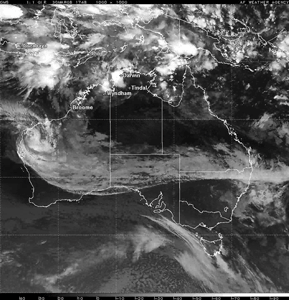 Tropical Cyclone Glenda (Courtesy: NRLMRY) |
Tropical Cyclone Glenda developed in the Timor Sea off the northern tip of Western Australia on the 27th. Glenda reached the coast of Western Australia on the 30th, making landfall near Onslow (located about 1,390 km or 860 miles north of Perth) with maximum sustained winds near 195 km/hr (105 knots or 120 mph). The cyclone prompted evacuations, closed oil fields and raised concerns of signficant flooding in the region (Reuters). |
For 2006 basin tropical cyclone statistics, please refer to the
following:
|


A major storm system that affected southeastern Europe during March 12-14 brought a variey of inclement weather to sections of Bulgaria, Romania and Greece and Turkey. In the Romanian capital of Bucharest, one person was killed and two injured when strong winds uprooted a tree. Around 50 automobiles were damaged due to downed trees caused by gusty winds. Strong winds cut power to over 300 towns across the country. Flooding also affected the region, with thousands of homes flooded in parts of Bulgaria, Greece and Turkey (AFP/BBC News). |
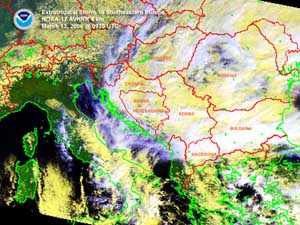 Storm System Over Southeastern Europe |


In the United Kingdom, an outbreak of cold, Arctic air affected northern sections of the country on the 1st. Snow fell across Northern Ireland, Wales and Scotland where accumulations of up to 12 cm (5 inches) were observed, forcing the closure of many schools and businesses. Temperatures fell to -6°C (21°F) at Sennybridge in Wales (BBC News). |
 Plains Snow Depth On March 21 |
A major winter storm affected the parts of the U.S. Great Plains during March 17-20. Heavy accumulations of snow affected a large area from parts of Colorado and Wyoming eastward into North and South Dakota and Kansas. Nebraska was particularly hard-hit, with snow accumulations of up to 76 cm (30 inches). The snow caused many travel disruptions and closed many schools and businesses (Associated Press). |
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
