Sea Ice Extent
| July 2015 | Sea Ice Extent | Anomaly 1991-2020 | Trend per decade | Rank (37 years) | Record | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| million km² | million mi² | Year(s) | million km² | million mi² | |||||
| Northern Hemisphere | 8.38 | 3.24 | -4.23% | -7.77% | Largest | 31st | 1983 | 10.57 | 4.08 |
| Smallest | 7th | 2012 | 7.67 | 2.96 | |||||
| Southern Hemisphere | 16.78 | 6.48 | +4.42% | +1.31% | Largest | 4th | 2014 | 17.11 | 6.61 |
| Smallest | 34th | 1986 | 15.32 | 5.92 | |||||
| Globe | 25.16 | 9.71 | +1.37% | -1.89% | Largest | 23rd | 1979 | 26.83 | 10.36 |
| Smallest | 15th | 2011 | 23.47 | 9.06 | |||||
Data Source: National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC). Period of record: 1979–2015 (37 years)
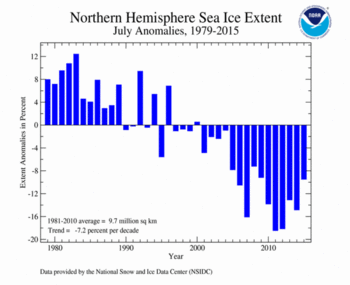
According to the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), the Northern Hemisphere sea ice extent — which is measured from passive microwave instruments onboard NOAA satellites — averaged for July 2015 was 8.77 million square km (3.39 million square miles), 920,000 square km (350,000 square miles), or 9.49 percent, below the 1981-2010 average. This was the eighth smallest July Arctic sea ice extent on record, but the largest since 2009. Arctic sea ice retreated at a near-average rate for most of the month, but accelerated at the end of July with the daily sea ice extent on July 31st within 550,000 square kilometers (212,000 square miles) of the record low extent on the same date in 2012. The Northern Sea Route was nearly open by the end of July, while the Northwest Passage continued to be impassable. Sea ice was below average in the Kara, Barents, Chukchi, East Siberian and Laptev Seas. Above-average sea ice was observed in Baffin Bay and Hudson Bay, which limited accessibility by sea to communities and research stations in the Arctic. Sea ice has been much below-average during the past several summers in Baffin and Hudson Bays. For the month of July, the Arctic sea ice extent is decreasing at an average rate of 7.0 percent per decade.
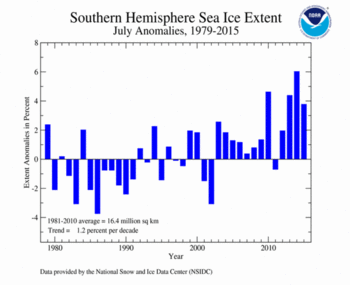
The July 2015 Southern Hemisphere sea ice extent was 17.06 million square km (6.59 million square miles), 620,000 square km (240,000 square miles), or 3.77 percent, above the 1981-2010 average. This was the fourth largest July Antarctic sea ice extent on record, behind 2014, 2010, and 2013. Sea ice expanded rapidly early in July, but slowed towards the end of the month due to regional ice retreat in the northern Weddell Sea and northwestern Ross Sea. On July 31st the daily sea ice extent was near the 1981-2010 average. July Antarctic sea ice extent is increasing at an average rate of 1.2 percent per decade.
When combining the Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere sea ice extents, the globally-averaged sea ice extent during July was 25.83 million square km (9.97 million square miles), 1.15 percent below the 1981-2010 average and the 15th smallest July global sea ice extent on record. This was the largest July global sea ice extent since 2004. July global sea ice extent is decreasing at an average rate of 1.84 percent per decade.
For further information on the Northern and Southern Hemisphere snow and ice conditions, please visit the NSIDC News page.
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information