NH Snow Cover Extent
Data were provided by the Global Snow Laboratory, Rutgers University. Period of record is 1966-2011 (46 years).
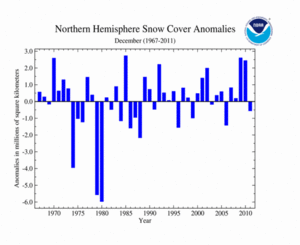
The Northern Hemisphere snow cover extent during December 2011 was below average, marking the 13th smallest December snow cover extent in the 46-year record. This is the first December since 2006 with below average snow cover for the Northern Hemisphere. During the month, the Northern Hemisphere snow cover extent was 42.7 million square km (16.5 million square miles) — 546,000 square km (210,800 square miles) below average.
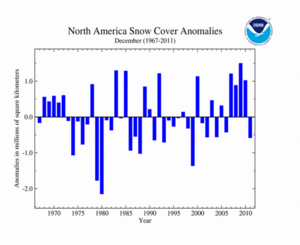
During December, the North American snow cover extent was below average, ranking as the 11th smallest December snow cover extent on record. This was the first December with below-average snow cover for North America since 2006. The monthly snow cover extent was 16.1 million square km (6.2 million square miles) — 569,000 square km (216,700 square miles) below average. During the month, several storms impacted the Southern Rockies of the U.S., causing above-average snow cover there. The rest of the U.S. generally had below-average snow coverage during the month. Canada had slightly above-average snow cover, with above average snow across the Canadian Rockies.
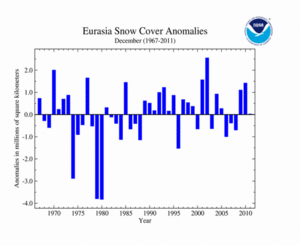
Eurasian snow cover was near-average in December, 23,000 square km (8,900 square miles) above the average of 26.6 million square km (10.3 million square miles), ranking as the 21st smallest (26th largest) monthly snow extent for the continent. This is the smallest December snow cover extent for Eurasia since 2008. Below-average snow cover was reported for most of Europe, with the exception of the Balkans. Below-average snow cover was reported for the Tibetan Plateau, the Himalayas, and western Asia. While above-average snow cover was observed across Turkey, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, and parts of central China.
Sea Ice Extent
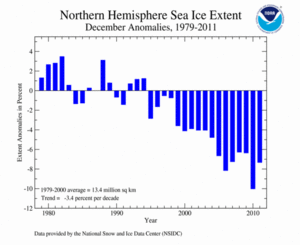
According to the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), the Northern Hemisphere sea ice extent — which is measured from passive microwave instruments onboard NOAA satellites — averaged for December 2011 was 12.38 million square kilometers (4.78 million square miles). This was 7.35 percent below the 1979-2000 average of 13.35 million square km (5.2 million square miles) and ranked as the fourth smallest December Arctic sea ice extent on record. December 2011 is the 17th consecutive December and 127th consecutive month with below-average Arctic sea ice extent. December Arctic sea ice extent has decreased at an average rate of 3.4 percent per decade.
Ice coverage during December was low across the Atlantic side of the Arctic in the Barents and Kara seas. The eastern portions of the Hudson Bay were not frozen over until the end of December; the bay is typically ice covered by the beginning of the month. Slightly-above-average ice extent was observed on the Pacific side of the Arctic, particularly in in Bering Sea.
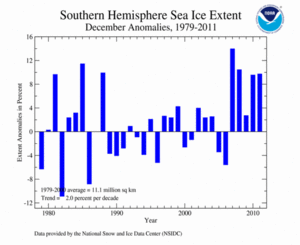
The December 2011 Southern Hemisphere sea ice extent was 9.77 percent above average — the 5th largest (29th smallest) December extent on record. This is the fifth consecutive December with above-average ice extent across the Antarctic. According to the NSIDC, unusually high sea ice was observed through much of December, in particular in the northern Ross Sea and the eastern Weddell Sea. Southern Hemisphere December sea ice has increased at an average rate of 2.0 percent per decade, with significant inter-annual variability.
For further information on the Northern and Southern Hemisphere snow and ice conditions, please visit the NSIDC News page.
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information