NH Snow Cover Extent
Analyses of NOAA data were provided by the Global Snow Laboratory, Rutgers University. Period of record is 1967-2009 (43-years).
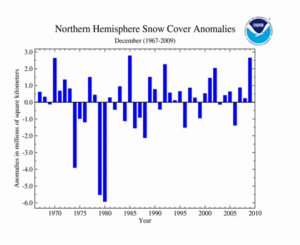
As shown in the time series to the right, the average Northern Hemisphere snow cover extent during December 2009 was above the 1967-2009 average. The Northern Hemisphere had the second largest snow cover extent, behind 1985, on record. The average Northern Hemisphere December snow cover extent for the 1967-2009 period of record is 43.2 million square kilometers.
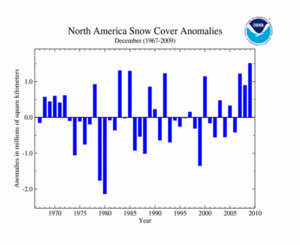
Across North America, snow cover for December 2009 was well above average, the largest extent since satellite records began in 1967. This can be attributed to several snow storms that swept across the continent, producing large snow accumulations. According to Environment Canada, Muskoka, Ontario, received 199.4 cm (78.5 inches) of snow during December 2009—more than twice the average monthly snowfall of 87.6 cm (34.5 inches). This value surpassed the previous record for most December snow of 194.6 cm (76.6 inches) set in 1985. Across the contiguous U.S., a major storm brought heavy snow across the eastern region, halting transportation and leaving thousands of residents without power. In the U.S. alone, numerous snowfall records for December were set. December 2009 had nearly 2,500 new daily records, 259 new monthly snowfall records, and 63 new all-time snowfall records. The average North American December snow cover extent is 16.6 million square kilometers for the period of record. Please visit the December Snow and Ice report and the U.S. Records page for more information.
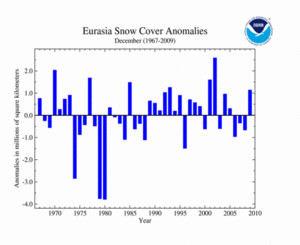
Eurasia's snow cover extent during December 2009 was above average, unlike the previous three years. This can be associated with anomalously cool conditions that enveloped much of northern Asia. December 2009 was the seventh largest December snow cover extent on record. The average Eurasian snow cover extent in December is 26.6 million square kilometers for the period of record.
Sea Ice Extent
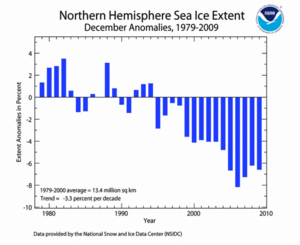
According to the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), the December 2009 Northern Hemisphere sea ice extent—which is measured from passive microwave instruments onboard NOAA satellites—was 12.5 million square kilometers (6.6 percent or 920,000 square kilometers below the 1979–2000 average), resulting in the fourth lowest December sea ice extent since satellite records began. When compared to December 2007—the record low—2009 was 210,000 square kilometers above the record low. This was the 15th consecutive December with sea ice extent below average. December 1994 was the last year that had above-average sea ice extent. December Arctic sea ice extent has decreased at an average rate of 3.3 percent per decade since 1979. Arctic sea ice usually expands during the cold season to a March maximum, then contracts during the warm season to a September minimum.
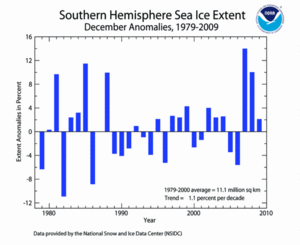
Meanwhile, the December 2009 Southern Hemisphere sea ice extent was 2.1 percent above the 1979–2000 average. This was the 14th largest sea ice extent in December. Southern Hemisphere sea ice extent for December has increased at an average rate of 1.1 percent per decade. Antarctic sea ice usually expands during the cold season to a September maximum, then contracts during the warm season to a March minimum.
For further information on the Northern and Southern Hemisphere snow and ice conditions, please visit the NSIDC News page, provided by NOAA's National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC).
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information