Northern Hemisphere Snow Cover Extent
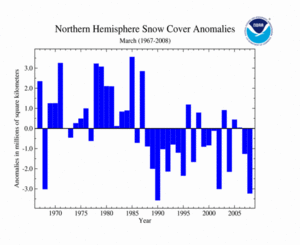
As shown in the time series to the right, the mean Northern Hemisphere snow cover extent during March 2008 was below average. During March, snowfall across the Northern Hemisphere was variable. In the contiguous U.S., multiple snow storms swept across the nation prompting numerous daily records and seasonal records. But across the Eurasian continent, unusually warm temperatures led to rapid snow melt. The Northern Hemisphere had the 2nd least snow cover extent on record, behind 1990. Heavy snowfall events in the U.S. during March 2008 prevented the Northern Hemisphere from having the least snow cover extent. The mean Northern Hemisphere March snow cover extent for the 1967-2008 period of record was 40.9 million square kilometers.
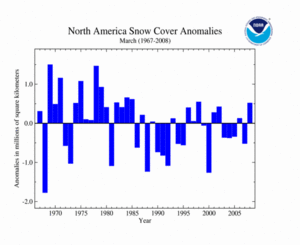
Across North America, snow cover for March 2008 was above average, the 10th largest extent since satellite records began in 1967. The mean North America March snow cover extent was 15.8 million square kilometers for the 1967-2008 period of record. Winter storms brought heavy snow across parts of the U.S. During March 7-9, a winter storm dumped heavy accumulations of snow from the lower Mississippi Valley to New England. The largest accumulation from this winter storm occurred in Columbus, Ohio, where the storm dumped over 51 cm (20 inches) of snow, setting a new event record. Also, snow that fell during March prompted several new seasonal total snowfall records. In Wisconsin, a winter storm that swept through on March 21 left snow accumulations of 13-46 cm (5-18 inches). This resulted in a new all-time seasonal snowfall for Madison, with a total of 254.2 cm (100.1 inches) of snow. Overall, the U.S. saw a total of 44,156 daily snowfall records (34,728 broken and 9,428 tied) during March 2008. Eliminating those stations that reported a trace of snowfall, the number of daily snowfall records would be 1,244 (907 broken and 337 tied).
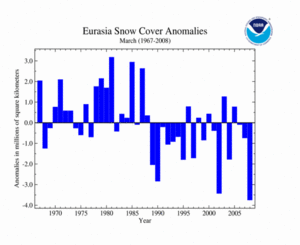
As depicted in the time series to the right, Eurasia's snow cover extent during March 2008 was below average. This was the least snow cover extent over the 41-year historical period. Much of this can be attributed to the above normal temperatures that covered most of the Asian continent. On average, the Eurasian snow cover extent in March was 25.1 million square kilometers for the 1967-2008 period of record.
Data were provided by the Global Snow Laboratory, Rutgers University.
Sea Ice Extent
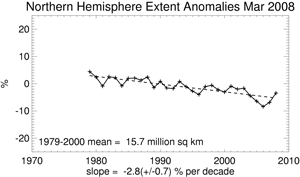
According to the National Snow and Ice Data Center, the March 2008 Northern Hemisphere sea ice extent, which is measured from passive microwave instruments onboard NOAA satellites, was below the 1979-2000 mean, but greater than the previous four years. This was the sixth least March sea ice extent on record. The past four years had the least March sea ice extent since records began in 1979. Sea ice extent for March has decreased at a rate of 2.8%/decade (since satellite records began in 1979) as temperatures in the high latitude Northern Hemisphere have risen at a rate of approximately 0.37°C/decade over the same period.
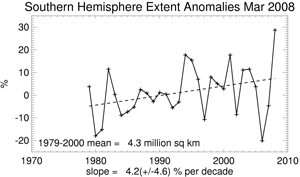
Meanwhile, the March 2008 Southern Hemisphere sea ice extent was much above the 1979-2000 mean. This was the largest sea ice extent in March (28.6% above the 1979-2000 mean) over the 30-year historical period, surpassing the previous record set in 1994 by 10.9%. Sea ice extent for March has increased at a rate of 4.2%/decade.
For further information on the Northern and Southern Hemisphere snow and ice conditions, please visit the NSIDC News page, provided by the NOAA's National Snow and Ice Data center (NSIDC).
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information