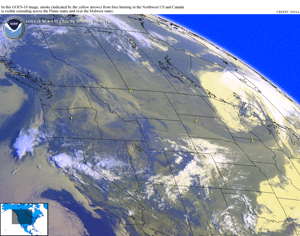
During September, wildfire activity decreased sharply across the western U.S. In particular, fire activity diminished across the Northern Rockies during the first half of September, where numerous large fires had been burning at the beginning of the month. Early in September, large fires across the Northwest and Northern Rockies generated a significant smoke pall, which was visible by satellite imagery moving east into the Midwest. By the end of the month, year-to-date wildfire activity remained below the ten-year average for the number of fires and acres burned (see table below). As of September 30th across the western U.S., the Northern Rockies region had the largest number of acres burned for the season (908,464 acres), followed by Alaska (574,723 acres), the Northwest Region (387,549 acres), the Eastern Great Basin Region (349,932 acres), the Southwest Region (264,491 acres), and Northern California (123,179 acres). At the end of September, Northern California was the primary focus of large fire activity in the nation, where several large fires were still actively burning.
| As of September 30 | Nationwide Number of Fires | Nationwide Number of Acres Burned |
|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 49,397 | 3,190,239 |
| 2002 | 67,424 | 6,657,049 |
| 2001 | 63,221 | 3,229,179 |
| 10-year Average | 69,222 | 3,955,472 |
Seasonal (January 1-September 30th) wildfire statistics, according to the National Interagency Fire Center are in the table to the right.
 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information