|
|
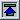
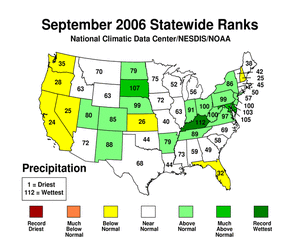
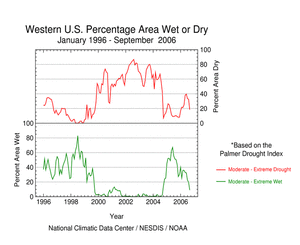
By the end of September,
drought was concentrated in the northern Plains, Texas and
northeastern Minnesota. Conditions had improved in most of the
Southeast and in the Southwest (September 26 Drought
Monitor). In the primary drought areas, soil
moisture was low, evaporation
was high, vegetative
health was poor, and
streamflow was low.
Drought impacted many sectors of the economy. Crops were highly
stressed or dying, livestock was dying or prematurely sold because
of a lack of feed and water, and water restrictions were common in
many areas. Disaster conditions have been declared by the governors
of several states.
Texas ended its worst fire season, which began in January 2005,
but burning bans continue in 103 counties. In Nebraska, drought is
estimated to have cost the agricultural community $350 million. In
South Dakota honey production was low, and wheat production was
down 37 percent. Low flows in the Missouri River prematurely ended
the navigation season, which usually ends around the beginning of
December. A positive impact of drought was the improved rice crop
in north central and northeastern Minnesota. Impacts in
drought-stricken areas have been collected and summarized by county
at the National Drought Mitigation Center's
Drought Impact Reporter.
The September precipitation pattern at the primary stations in
Alaska
was below average across the interior of the state; the coastal
stations were above average. In Hawaii
dryness continued throughout most the State. In Puerto
Rico the month was predominantly dry along the southern coast
(based on National
Weather Service radar estimates of precipitation).
|
|
Some regional highlights:
|

 NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information
NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information